General
Are you trading company of manufacturer?
Established in 2010, Haibo Electrical Equipment Co.,Ltd. is situated in Cixi, Ningbo, a strategic location in the Yangtze River Delta region. This coastal economic open area, approved by the State Council of China, is known for its industrial and commercial significance in the southern Greater Shanghai Economic Circle.
Haibo is a manufacturer that specializes in producing top-of-the-line household electrical appliances, such as the Soda Water Maker, Free Standing Water Dispenser, and Countertop Water Dispenser. The company has consistently enhanced and refined its various processes and now boasts a comprehensive quality control system, encompassing product R&D and design, incoming material inspection, production organization, product shipment, and after-sales service. Furthermore, customer feedback and suggestions are highly valued and implemented to further improve our products.
What are your main products?
Haibo is a leading manufacturer specializing in water purifiers,soda makers, and water dispensers for over 15 years.
How can I become a distributor for your products?
Please contact us directly through our website for information on becoming a distributor. We are eager to collaborate with partners who share our commitment to quality hydration solutions.
Can I sell your soda maker as a distributor?
Yes, but please note that to sell our soda maker, you must have access to a reliable gas supply to provide the necessary gas cylinders for your customers.
Do you do customization? What is the MOQ?
Yes, we provide OEM & ODM service for our customers. The MOQ varies for different products. Please contact us for further discussion of details via mail or Whatsapp.
What Is The Lead Time?
Sample Needs 4~5 Days, Mass Production Needs 10-15 Days, It According To Quantity.
Product
What is the filtration process in your water dispensers?
Our dispensers include a comprehensive 4-stage filtration system, consisting of a PP filter for large particles, a GAC filter for residual chlorine, a UF or RO membrane for bacteria and microorganism
Are the water dispensers suitable for commercial use?
Absolutely! Our freestanding water dispensers are ideal for offices, restaurants, and other commercial settings, providing efficient hydration solutions for larger groups.
What control options are available for the water dispensers?
We offer different models with touchscreen controls and mechanical faucet options, allowing you to choose the one that best fits your preference.
Do you provide gas cylinders for the soda maker?
Please note that we do not include filled gas cylinders with our soda maker. Instead, our product requires specific air cylinders. It is the responsibility of our customers to ensure they have a stabl
What features does the soda maker have?
Our portable soda water machine allows for the creation of carbonated drinks and nitrogen-infused coffee. It also has the ability to connect with a milk frother for increased flexibility.
How do the water dispensers connect to the water supply?
Our water dispensers are POU (Point of Use) machines that connect directly to your water pipes, eliminating the need for bulky bottled water.
What temperature options are available for your water dispensers?
Our water dispensers provide three temperature options: hot, cold, and room temperature, catering to all your hydration needs.
What types of water dispensers do you offer?
We provide both freestanding and countertop water dispensers, each featuring a 4-stage filtration system. Customers can select between ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis choices.
What is the filtration process in your water dispensers?
Our dispensers come equipped with a 4-stage filtration system consisting of a PP filter to remove large particles, a GAC filter to eliminate residual chlorine, either a UF or RO membrane to block bacteria and microorganisms, and a T33 filter to improve the water's taste.
When Should the RO Membrane Be Changed?
The membrane will have a lifespan of at least two years if the pre-filters are routinely changed when necessary. If you observe a gradual decrease in water output, it could be due to a buildup of minerals and salts on the membrane's surface. A gradual decline in water quality may signal damage to the membrane and necessitate replacement.
Note: For enhanced accuracy in determining when to replace the membrane, the quality of both the feed and product water can be tested using a TDS tester. This reliable tool provides valuable insights for optimal performance.
How Often Should the Filters and RO Membrane Be Changed?
Adjust the filter change time for all filters and the RO membrane to meet the local water conditions. Typically, this can be done for water with TDS levels of 300 ppm or lower using the following guidelines.
- RO membrane: every 2 years
- Pre-filter PP5u: every 3 months
- Sediment PP 1u: every 9 months
- Post Carbon: every 12 months
- Carbon: every 6 months. (Note: It is important to change this cartridge every 6 months to prevent chlorine in the feed water from damaging the membrane.)
For optimal performance, it is recommended to replace filters more frequently when dealing with water that has a higher level of TDS.
Factors that May Affect the Quality and the Quantity of the Water Produced
TEMPERATURE. For optimal results when using RO, the ideal water temperature is 25°C (76°F). It should be noted that if the water temperature drops below 4°C (40°F), the production of RO will be significantly reduced. Additionally, to avoid any potential damage to the membrane, it is recommended to keep the maximum water temperature below 35*C (95*F).
PRESSURE. Ensure optimal water production and quality by maintaining water pressure above 60 PSI. The addition of a Haibo booster pump to your system will guarantee consistent pressure levels on the membrane.
MEMBRANE. Customized membranes are tailored to specific contaminant rejection rates, production speeds, and resistance to chemical decay. Haibo is able to provide the most suitable membrane for your particular feed water circumstances and filtration requirements.
TOTAL DISSOLVED SOLIDS (TDS). In most cases, the TDS of tap/feed water should not exceed 500 ppm (parts per million). Higher levels of TDS may decrease the amount of water produced and result in a higher TDS in the product water. A booster pump can be used to increase pressure on the membrane and improve the volume and quality of product water if the inlet water has a high TDS level.
Why Does an RO System Have Five or More Stages in the Filtration Process? What is the Purpose of Each Step?
The first filter is a 5-micron particle filter designed to eliminate dirt, rust, and other sediment.
The second carbon filter serves as a crucial component by effectively eliminating various organic chemicals and, most notably, chlorine from the water to prevent potential damage to the RO membrane.
Third is a high-quality, highly efficient filter with a 1-micron rating that effectively removes even the smallest particles that may have been missed by the carbon filter.
Fourth, the RO membrane, which is essential to the system, will remove 95-99% of dissolved contaminants from the water. These contaminants are then washed away, and the pure water is then stored in a pressurized tank.
Fifth, the storage tank is followed by a carbon filter that effectively "polishes" the water, removing any lingering odors or flavors before it reaches the faucet.
Optionally, the addition of a remineralizing filter can be considered as a sixth stage, or it can be paired with the fifth stage carbon filter to create a combination (fifth stage) “polishing-remineralizing” filter.
What is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse osmosis is a water filtration technique that employs pressure on a semi-permeable membrane to reverse the natural flow of osmosis. Osmosis is a naturally occurring event that transpires across various membranes in the human body. While water molecules can pass through the membrane, salts are unable to do so. In the presence of differing salt concentrations on either side of a membrane, water will move from the side with lower salt concentration to the side with higher salt concentration, creating pressure on the latter. By applying this principle, RO can effectively remove contaminants and salt from a water solution, producing pure water on the other side of the membrane. As the water flow is reversed from its natural course, this process is known as reverse osmosis, or RO for short.
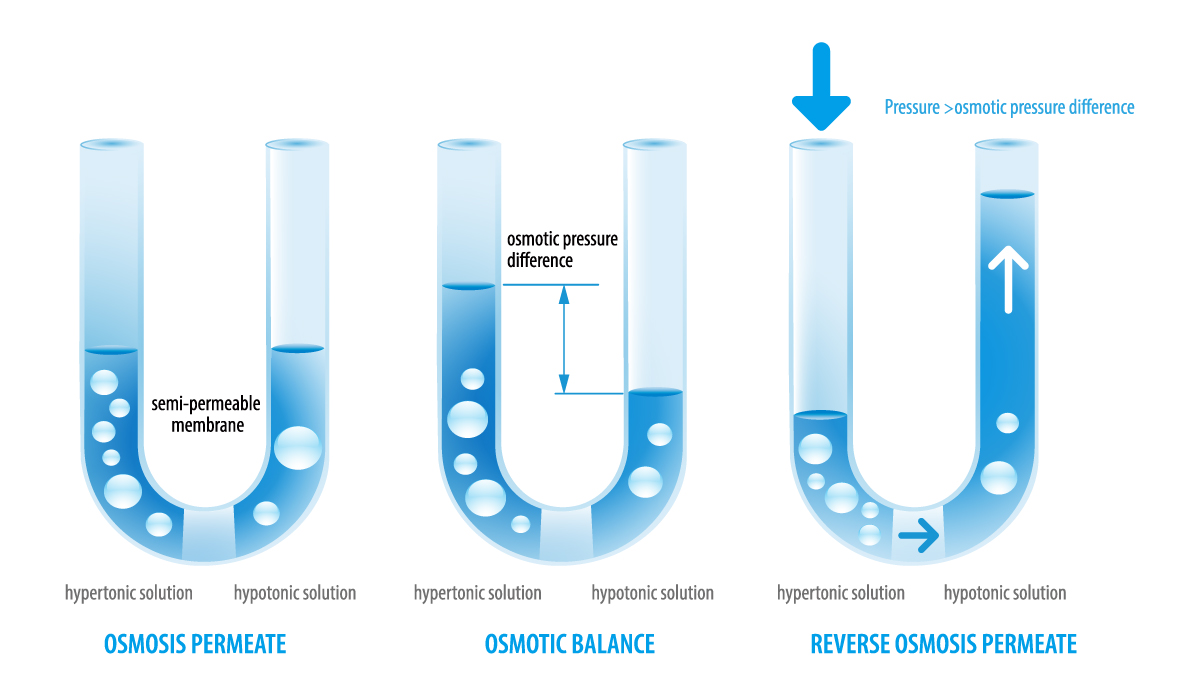
What is the Difference Between a Regular Water Filter and Reverse Osmosis?
There are two major differences between filtration and reverse osmosis:
- The use of a regular filter means that all water will pass through, resulting in particles collecting and potentially blocking the filter. On the other hand, RO filtration has the feed water flowing across the membrane's surface instead of passing through it entirely. This allows for impurities to be washed away from the membrane's surface and out to the drain, ensuring the membrane remains free from contaminants and prolonging its lifespan. Additionally, this process guarantees the purity of the filtered water by constantly removing impurities from the membrane.
- Ordinary water filters effectively remove dirt and sediment particles from water, typically down to one micron. However, they cannot remove dissolved chemicals. In contrast, reverse osmosis employs a polymer membrane to filter down to the molecular level, eliminating dissolved chemicals and salts that traditional filters cannot.
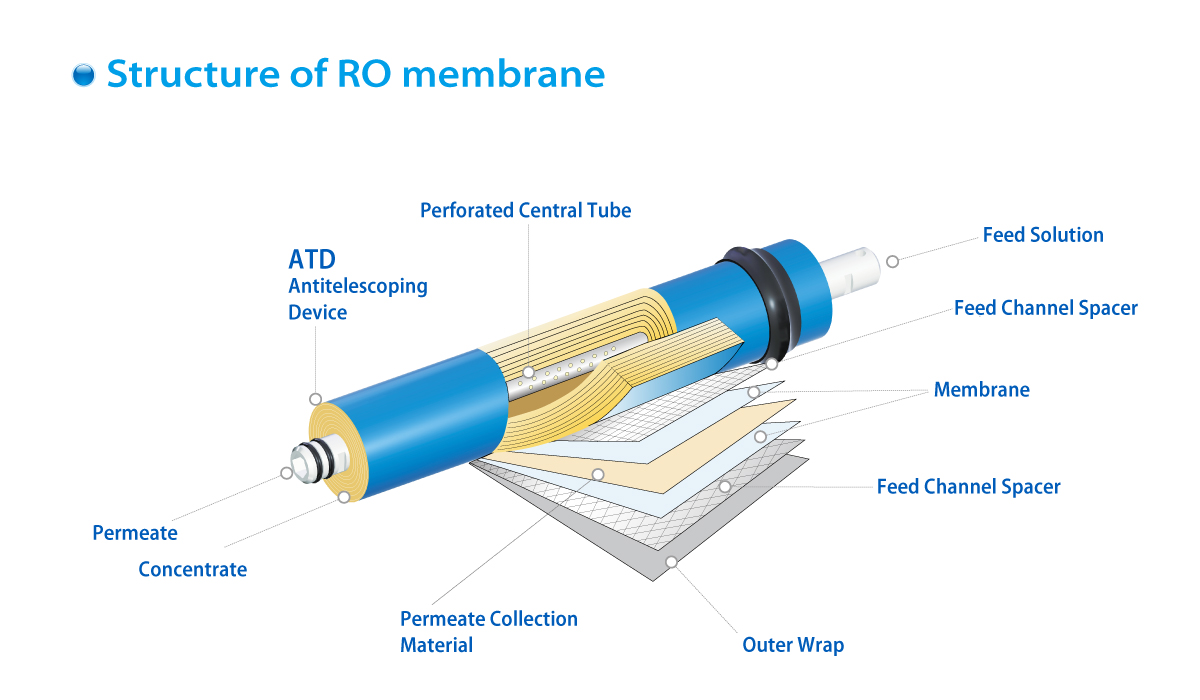
What is the RO Membrane Made of and How Does It Work?
The RO membrane is composed of a delicate film that performs the filtration process, sandwiched between supportive layered sheets. This is referred to as the "Thin Film Composite" or TFC membrane. It is wrapped in a spiral shape around a plastic tube, allowing pure water to be gathered at the center while impure water exits through the end of the membrane tube to the drain.
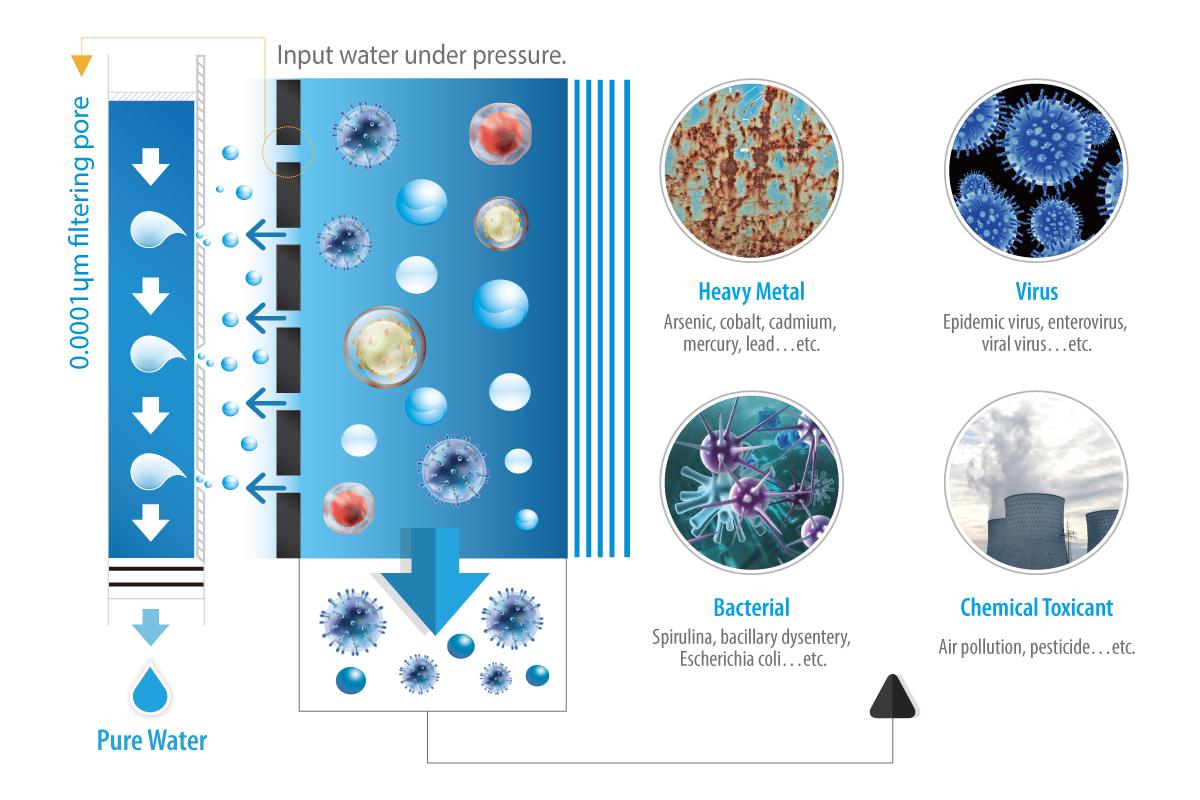
What Contaminants Does Reverse Osmosis Remove?
The RO membrane effectively removes at least 96% of organic contaminants and chemicals found in water, including DBCP, PCBs, THMs, TCE, lead, copper, zinc, arsenic, nitrates, and other organics. This is achieved through an industrial-level filtration process.
Does RO Remove Sodium from Water?
YES! Reverse Osmosis was initially created to remove salt from seawater in order to make it usable for consumption.
For individuals following a low-sodium diet, consider RO as the optimal method for removing sodium, especially from treated water.
